
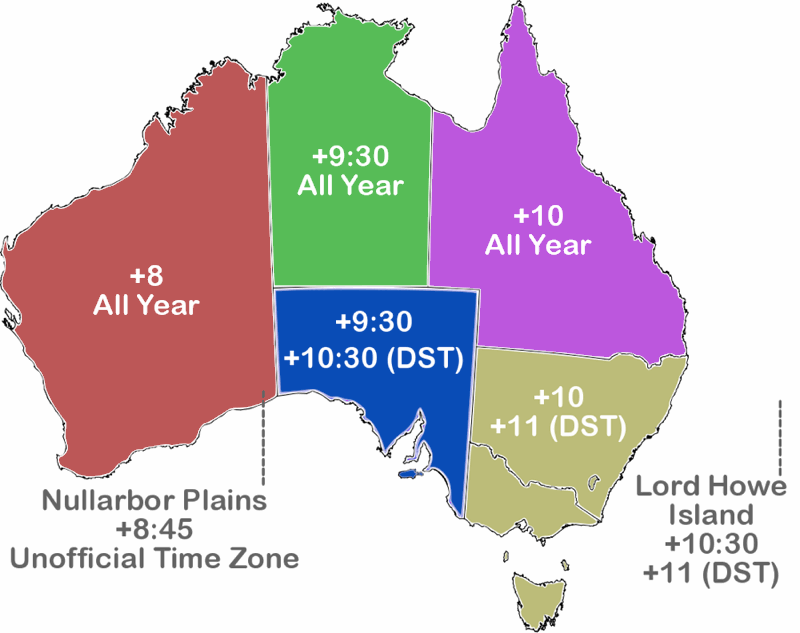
In accordance with the Coordinated Universal Time or UTC, the AEST is calculated by adding ten hours to the UTC (UTC +10:00). The cities that AEST covers are Brisbane, Sydney, Melbourne, Hobart, and Canberra. The Australian eastern standard time or AEST covers the states and territories of Queensland, New South Wales (except Brooklyn Hill), Victoria, Tasmania, and the Australian capital Territory. Let us have a glance through each of them: It is demarcated as the world’s sixth largest country.īeing such a large country, there are mainly three separate time zones. How many time zones are there in Australia?Īustralia has a total land mass of about 7.7 million square centimeters. Now that we know what time zone is, let us directly dive into the time zones of Australia.Ģ. They add an hour to the local time in two seasons, namely spring and summer for just a part of the year. If the answers to these questions account to yes, you have made it to the correct article which will be a complete guide for you to know everything about the time zones in Australia and even how it is converted! So make sure to stick around till the end to find out more about the time zones in Australia!īefore we delve directly into the subject, let us quickly understand the concept of time zones and why they exist.Īccording to Wikipedia, a time zone is “an area that observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes.” There are certain areas that are in higher latitudes and they use daylight saving time. It is worth noting that the Northern Territory remains on Australian Central Standard Time all year long as they do not observe Daylight Saving.Are you intrigued to know what the time zone of Australia is? Do you want to know how many time zones there are in Australia? Whatever is your reason, knowing a country’s time zone before you migrate is compulsory. Locations in Australian Central Time Zone This means there is a 30 minute difference in local time from the actual one-hour time zone interval you’d usually see if traditional time standards were used. As soon as Daylight Saving begins – during the summer – the affected territories switch to Australian Central Daylight Time or ACDT.Īustralian Central Standard Time and Australian Central Daylight Time are non-standard half-hour time zones. The time zone is primarily observed by territories and states in Australia during the winter months when Daylight Saving is inactive. This means that the time zone is 9 and a half hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. Australian Central Standard TimeĪustralian Central Standard Time or ACST has a UTC offset of +9:30. After Daylight Saving is over – during the winter – the affected territories switch to Australian Central Standard Time or ACST. The time zone is primarily observed by territories and states in Australia during the summer months when Daylight Saving is active. This means that the time zone is 10 and a half hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. Australian Central Daylight TimeĪustralian Central Daylight Time or ACDT has a UTC offset of +10:30. Because of that, Australian Central Time is not static and it switches depending on whether or not Daylight Saving is active. Australian Central Time or ACT is a blanket term used to describe the local time observed in both the Australian Central Daylight Time (ACDT) and Australian Central Standard Time (ACST) zones.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
